Latest Arc Flash Articles

When is Equipment Labeling Required for Arc Flash Hazards?
Equipment labeling for arc flash hazards is required by NFPA 70E and OSHA when energized electrical equipment poses a risk. Labels must display voltage, incident energy, and PPE requirements to protect workers from arc flash and shock hazards.
When is equipment labeling required for arc flash hazards?
OSHA regulations and NFPA 70E outline this requirement—the standard for electrical safety in the workplace. Labels are critical for warning workers about shock and arc hazards and for specifying the personal protective equipment (PPE) needed to perform tasks safely. Failure to provide accurate identification can result in serious injury and non-compliance penalties.…
View more
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
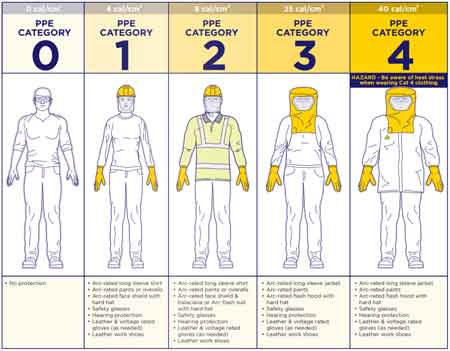
Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart
Arc flash categories by voltage chart shows required PPE levels based on system voltage and incident energy. This guide helps electrical workers select appropriate protection according to NFPA 70E standards, reducing shock and arc flash risks in industrial and commercial settings.
Quick Reference: Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart
For a foundational overview of arc flash risks, see our main arc flash guide, which covers causes, hazards, and safety strategies.
This chart categorizes different voltage levels and their associated risks, guiding workers and safety professionals in selecting the appropriate level of protection. Higher voltage levels generally correspond to higher energy…
View more

OSHA 1910.333: Safety-Related Work Practices
OSHA 1910.333 outlines safety practices for working on or near exposed energized electrical conductors and circuit parts. It ensures proper de-energization, lockout/tagout procedures, and qualified personnel requirements to reduce electrical shock, arc flash, and burn hazards.
Essential Guide to OSHA 1910.333 for Electricians
NFPA 70E Arc Flash Training
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
OSHA 1910.333, formally known as the Work Practices Standard (29 CFR 1910.333), is a cornerstone of electrical safety in workplaces across the United States. Established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, this regulation outlines safety-related work practices to protect workers…
View more

Arc Flash Meaning Explained
Arc Flash Meaning explains the hazardous energy released by arc faults in switchgear and panels, guiding electrical safety per NFPA 70E, incident energy calculations, PPE selection, short-circuit studies, and effective arc flash hazard analysis.
Understanding Arc Flash Meaning in Electrical Safety
Arc Flash Meaning - Simply put, it is a sudden release of energy due to an arcing fault between electrical conductors or between a conductor and a ground. This arc flash event occurs when an electrical arc forms, creating a high-temperature plasma that can cause severe damage and injury. An arc flash (AF) typically happens when energized electrical equipment…
View more

What is Lockout Tagout? Energy Control
Lockout Tagout is a critical safety procedure that protects workers by controlling hazardous energy during equipment servicing. It ensures proper shutdown, isolation, and secure tagging to prevent accidental startup and electrical hazards.
What is Lockout Tagout?
NFPA 70E Arc Flash Training
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Lockout Tagout in Practice
The process typically involves five critical steps: identifying energy sources, shutting down equipment, applying lockout devices, attaching warning tags, and verifying that energy has been isolated. Authorized employees apply locks and tags, while affected employees are trained to recognize and respect them. These steps ensure…
View more

What is Arc Flash?
Arc flash is a sudden electrical explosion that occurs when fault current travels through air between energized conductors or to ground, forming an electric arc. The arc releases extreme heat, intense light, and a pressure wave that can cause severe burns, hearing damage, and catastrophic equipment destruction in milliseconds. Arc flash severity is primarily determined by available fault current, protective device clearing time, working distance, and equipment configuration, which is why incident energy analysis is used to quantify risk.
In North America, arc flash hazards are governed by NFPA 70E in the United States and CSA Z462 in Canada. These…
View more
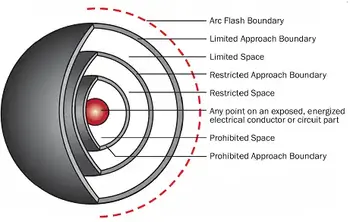
Arc Flash Boundary Explained
An arc flash boundary is the distance from an energized electrical source at which the incident energy equals 1.2 calories per square centimeter, the threshold for a second-degree burn specified in NFPA 70E Article 100.
This boundary defines where specialized arc-rated PPE and controlled work planning are required under NFPA 70E. It is not a theoretical safety buffer, but a calculated control used in hazard analysis, job planning, and energized work authorization.
Inside the arc flash boundary, the work stops being routine, even if the task looks routine. Entry into this zone changes who may approach the equipment, what protective…
View more