Smart Grid
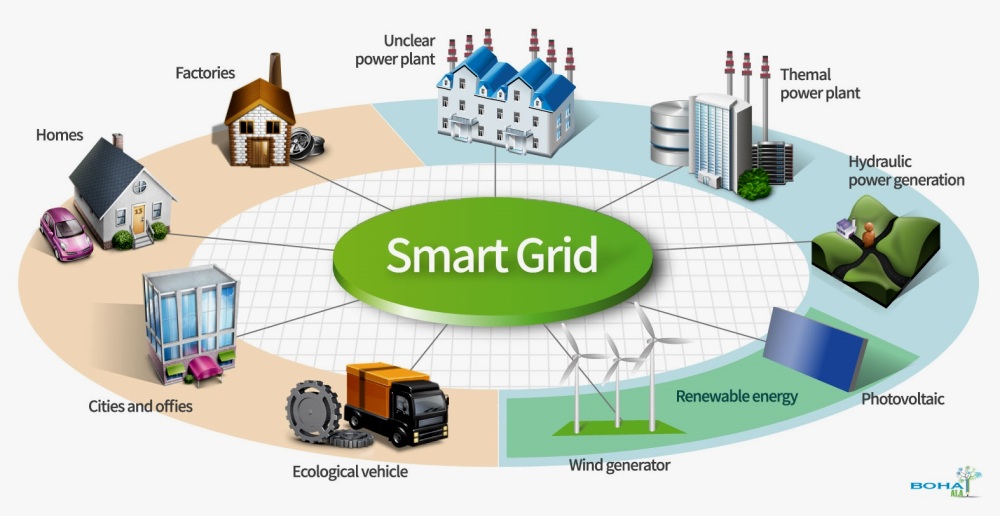
Grid Modernization Explained
Download Our FREE Smart Grid Handbook

Automation of T&D Systems Handbook
This 100+ page handbook is filled with the very latest practical information on SCADA, substation automation, automated mapping/facilities management (AM/FM), and geographic information systems (GIS). This book is ideal for utility T&D automation specialists.
The automation of T&D systems involves the integration of advanced technologies such as real-time monitoring, remote control, fault detection, and predictive analytics to enhance grid performance, reliability, and safety. In this handbook, we explore the fundamental principles behind the automation of power transmission and distribution, along with the latest innovations in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, Distribution Management Systems (DMS), and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). We also cover the impact of smart grid technologies, renewable energy integration, and the growing role of digitalization in modernizing electrical networks.
Designed for electrical engineers, system operators, planners, and researchers, this resource provides a thorough understanding of the strategies, tools, and technologies used to automate T&D systems, improve operational efficiency, and ensure grid stability. With a practical approach to real-world applications, the handbook highlights the benefits of automation in reducing operational costs, minimizing downtime, and enhancing fault detection and recovery.
As the global energy landscape evolves, the Automation of T&D Systems Handbook offers crucial insights into how automation is revolutionizing the way we manage and distribute electricity. This guide is an invaluable resource for professionals looking to stay ahead in the rapidly advancing field of smart grid technology and the automation of electrical systems.
Latest Smart Grid Articles
Substation SCADA
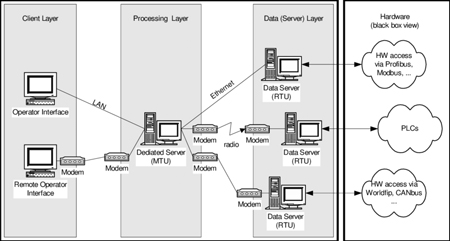
SCADA Architecture

SCADA Cybersecurity
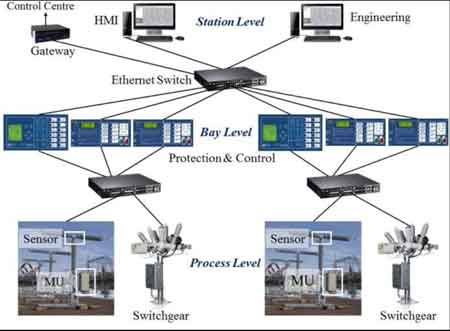
Smart Substation and the Evolving Grid
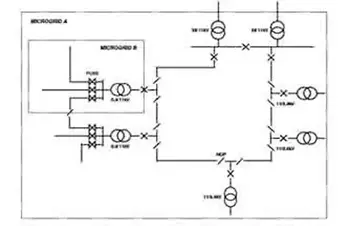
Coordinated Protection, Control Automation Schemes

SCADA Monitoring
Smart Grid News
Smart Grid Media
Smart Grid Articles From ET Magazine

AI at the Substation Edge: Digital Twins and Predictive Maintenance for Transformers and Switchgear

Deterministic Communications for Protection: TSN + Private 5G from the Yard to the Control Room

Inside the Digital Substation Upgrade: Migrating to IEC 61850 Ed. 2.1, Process Bus, and Interoperable Testing

Zero-Trust Substations: How CIP Is Shifting from Perimeter Defense to Continuous Vendor and Supply-Chain Risk Management
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Smart Grid Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Smart Grid Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue