Who Can Enter Limited and Restricted Boundaries?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training – Electrical Safety Compliance Course
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
Who can enter limited and restricted boundaries is defined by NFPA 70E and OSHA rules. Only qualified electrical workers with training, PPE, shock protection, and work permits may cross approach boundaries during energized work.
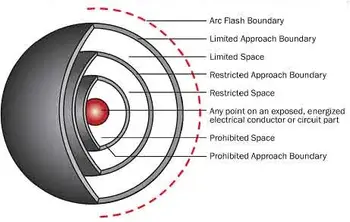
Limited and Restricted Boundaries Explained
Electrical safety is paramount in workplaces with energized electrical equipment. A critical aspect of ensuring safety is understanding and adhering to protection boundaries established around such equipment. These boundaries, namely the limited approach boundary and restricted approach boundary, define safe distances from exposed energized conductors or circuit parts and dictate who can enter these zones. NFPA 70E defines how approach boundaries are established, and the distinctions between limited, restricted, and prohibited zones are explained clearly on the NFPA 70E approach boundaries page.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Ensuring electrical safety in the workplace involves understanding and respecting arc-flash and shock protection boundaries as outlined by NFPA 70E. These boundaries define safe distances from exposed energized conductors or circuit parts and dictate who can enter these areas and under what conditions. This article explores who can enter limited and restricted boundaries, the criteria for crossing these boundaries, how to determine them, and the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) required.
Workers entering limited or restricted boundaries must be properly trained, and the scope of that training is outlined in the NFPA 70E training requirements.
Limited Approach Boundary: This boundary is established to protect individuals from shock hazards. It marks the closest distance that an unqualified person can approach exposed energized conductors or circuit parts without being accompanied by a qualified person.
- Qualified Workers: Only workers who have been trained and can recognize and avoid electrical hazards can enter the limited approach boundary unescorted. These workers are familiar with the appropriate safety procedures and the use of PPE.
- Unqualified Persons: Unqualified persons may cross the limited approach boundary only when escorted by a qualified person. This ensures that they are protected and do not inadvertently expose themselves to electrical hazards.
Restricted Approach Boundary: This boundary is closer to the energized parts and presents a higher risk. Entry into this area requires greater caution.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
- Qualified Workers: Only qualified workers may cross the restricted approach boundary; they must have a valid work permit and appropriate PPE for the specific electrical hazards present.
- Work Permit: A work permit is required to document and authorize the work within the restricted approach boundary. This permit ensures that all safety measures are in place and that the work is carried out safely.
- Selecting the correct protective equipment is critical when crossing approach boundaries, which is why understanding arc flash PPE categories is essential for qualified electrical workers.
Who May Cross the Limited Approach Boundary?
The limited approach boundary is designed to restrict access to those who are trained and knowledgeable about electrical safety. Qualified workers can cross this boundary without additional supervision, provided they adhere to all safety protocols and wear the necessary PPE. A qualified worker must accompany unqualified persons to ensure their safety. Approach boundaries are closely tied to incident energy levels, and tools such as an arc flash calculator help determine exposure risks before energized work begins.
How to Determine the Limited Approach Boundary?
Determining the boundary of the limited approach involves assessing the potential hazards posed by exposed energized conductors or circuit parts. According to NFPA 70E, the boundary is based on the electrical system's voltage rating and the potential for an arc-flash incident. The following steps are generally involved:
-
Identify Voltage Ratings: Determine the electrical equipment's voltage levels to assess risk.
-
Assess Potential Hazards: Evaluate arc-flash hazards based on the electrical system and its conditions.
-
Calculate Safe Distances: Use the NFPA 70E standardized tables and formulas to determine safe distances from exposed energized parts. These calculations help set the boundary of the limited approach at a distance where the incident energy is 1.2 calories/cm², a level sufficient to cause second-degree burns but not more severe injuries.
What to Wear in a Limited Approach Boundary?
When entering a limited approach boundary, the type of PPE required depends on the potential hazards identified during the risk assessment. The main goal is to protect workers from both shock hazards and arc flash incidents. The following PPE is typically recommended:
-
Voltage-rated gloves: To protect hands from electrical shocks.
-
Insulated Tools: To prevent accidental contact with energized parts.
-
Arc-Rated Clothing: Depending on the potential arc flash hazard, clothing with appropriate arc ratings (measured in calories/cm² of incident energy) should be worn to protect against burns.
-
Face Shields and Safety Glasses: To protect the face and eyes from potential arc flash and shock hazards.
Understanding who can enter limited or restricted areas and the conditions under which entry is allowed is crucial to maintaining electrical safety in the workplace. Qualified workers, equipped with the appropriate training and PPE, are authorized to enter these high-risk areas, while a qualified person must escort unqualified persons. Determining the boundaries involves careful assessment of the voltage ratings and potential hazards, ensuring that the appropriate protection measures are in place. By adhering to NFPA 70E standards and implementing strict safety protocols, workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of electrical injuries and ensure a safer working environment for all employees.
Related Articles