Electrical Protection
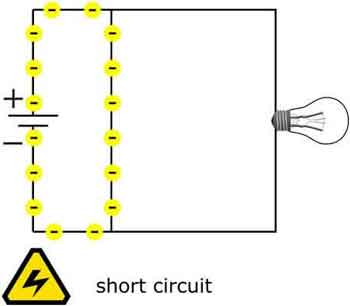
Short Circuit Protection Explained
Download Our FREE Electrical Protection Handbook

Circuit Breaker & Switchgear Handbook, Vol. 4
This fourth edition of our popular circuit breaker and switchgear series explores in detail circuit breaker and switchgear functions, maintenance, protection and operations. Articles including Magnetic Actuated Circuit Breaker Reality, Applying Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers to Limit Arc Flash, and Enhancing Workplace Safety with Medium Voltage, Metal-Clad Arc Resistant Switchgear are but a few examples of the variety of subjects dealt with in this valuable 100 page book.
In Volume 4, we dive deep into the core principles and technologies behind circuit breakers and switchgear, covering everything from traditional technologies to the latest advancements in digital and smart systems. The book offers detailed insights into the various types of circuit breakers—air, oil, vacuum, SF6, and more—exploring their operational characteristics, design considerations, and selection criteria for different applications. We also examine the different types of switchgear, including medium- and low-voltage switchgear, and their roles in controlling and protecting electrical circuits.
This edition provides comprehensive coverage on the installation, testing, maintenance, and troubleshooting of circuit breakers and switchgear, offering practical guidance on optimizing performance, minimizing downtime, and ensuring compliance with the latest safety and regulatory standards. Case studies and real-world examples further enhance the reader's understanding of best practices and common challenges faced when implementing and maintaining circuit protection systems.
Latest Electrical Protection Articles
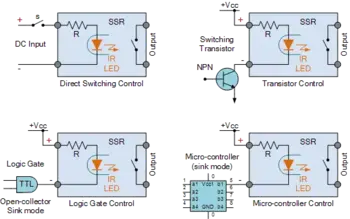
What Are The 7 Reasons to Opt for Solid State Relays?

Types of Short Circuit Faults in a Power System

Transformer Protection
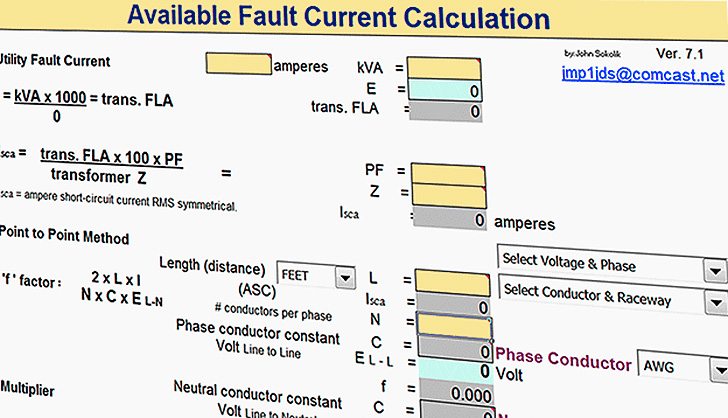
What is Fault Current
What Is A Electrical Relay?