Electrical Safety Hazards
By Howard WIlliams, Associate Editor

CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training – Electrical Safety Compliance Course
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards
- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
Electrical safety protects workers from shock, arc flash, and energized equipment hazards through grounding, PPE, lockout procedures, and safe work practices used in industrial and commercial environments.
Engineering is not a collection of rules waiting to be consulted after something goes wrong. It is the discipline that shapes how people interact with energy in environments where work is routine, time is constrained, and decisions are often made with incomplete information. Voltage, current, and stored energy behave predictably. Human judgment does not.
Request a Free Training Quotation
What makes power systems hazardous is rarely complexity alone. It is the ordinary conditions of real workplaces: equipment that has aged quietly, procedures that are assumed rather than verified, and tasks performed often enough that caution erodes without anyone noticing. In those settings, grounding, insulation, protective equipment, lockout practices, arc flash boundary and arc flash mitigation are not abstract safeguards. They are the difference between a normal shift and a permanent injury.
If your role regularly brings you into proximity with energized equipment, understanding how arc flash and related hazards develop alongside shock risk becomes essential. The Arc Flash channel provides a broader context for these exposure-driven dangers and how they intersect with everyday work.
Why Electrical Safety Is Important
Electrical safety is often described as the most important issue in the industry, but that phrase only becomes meaningful when viewed in context. Electricity underpins nearly every modern system, from industrial production lines and institutional facilities to communications infrastructure and residential environments. Because it is everywhere, it is also easy to underestimate.
Serious arc flash incidents rarely occur because electricity behaves unpredictably. They happen because people misjudge risk, work around safeguards, or assume that familiarity equals safety. Every year, workers and non-workers alike are injured or killed by electric shock, arc flash burns, and arc blast forces that develop in fractions of a second. For readers who want a clearer separation between heat injury and blast trauma, see Arc Flash vs Arc Blast. Protective equipment decisions are not arbitrary and should follow defined criteria, which is why arc flash PPE selection is governed by formal arc flash PPE requirements tied directly to incident energy and task exposure.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
The Hidden Risk of Accepted Exposure
In many cases, those injured were not unaware of the hazard in general. Some underestimated the effect of voltage and current on the human body. Others knew the risk but accepted it temporarily, trusting experience, speed, or habit. Electrical safety matters precisely because electricity does not forgive these judgments. This applies as much to non-qualified workers near energized systems as it does to licensed electricians performing complex tasks. When enforcement expectations are the issue, the clearest grounding point is OSHA electrical safety standards.
In practice, safety begins with organizational intent. Companies that treat safety as a living obligation invest in training, supervision, and maintenance long before an incident occurs. Professionals require periodic, recurring training that reflects how systems actually age, how facilities change, and how standards evolve. In the U.S., most programs translate electrical safety requirements into day-to-day methods through NFPA 70E. In Canada, the same role is played by CSA Z462, which aligns closely with NFPA 70E but is written for Canadian workplace practice.
Basic electrical safety awareness is often tested not during major installations, but in the everyday working environment where small decisions accumulate. Many accidents begin with overlooked details such as damaged extension cords, overloaded power cords, or power tools used beyond their intended limits. At the technical level, most workplace electrical safety programs rely on the framework established in NFPA 70E arc flash requirements, which define how hazards are evaluated, controlled, and communicated.
A ground fault does not announce itself in advance, and when it occurs, the consequences depend largely on how well routine conditions were managed beforehand. Paying attention to these ordinary factors is what separates controlled work from preventable injury.
Electrical Safety Protection Programs
Well-designed electrical safety protection programs reduce injury risk and equipment damage not by eliminating mistakes, but by anticipating them. When abnormal conditions arise, such as faults, failures, or emergency switching, the program defines how power is deliberately restored rather than how it is reacted to. Sound planning aligns task execution with electrical safety work practices that reduce exposure during testing, troubleshooting, and energization. When facilities want their program to reflect equipment-specific hazards rather than generic assumptions, they typically begin with an arc flash analysis.
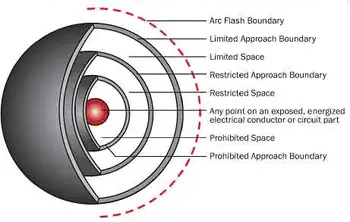
Understanding how close a worker can safely approach energized equipment is best illustrated by an arc flash boundary chart, which translates calculated risk into usable distance guidance.
In North America, employers carry clear legal responsibilities to maintain safe work conditions. Under occupational health and safety legislation, accountability is shared among employers, supervisors, and workers. Safety is not delegated entirely to specialists. Understanding applicable electrical safety requirements allows organizations to meet their legal duties in a way that reflects real operations rather than paper compliance.
Electrical Safety and OSHA Regulations
OSHA arc flash requirements govern arc flash hazards across general industry, shipyard employment, and marine terminals through a network of standards, interpretations, and enforcement guidance. These requirements are supported by regulatory agendas, federal register notices, and official interpretations issued to guide compliance officers and employers alike. National consensus standards complement this framework by addressing hazards associated with specific types of equipment and work conditions. When the conversation shifts from “rules” to measurable severity, incident planning typically returns to incident energy because it drives boundaries, PPE decisions based on arc flash ppe requirements, and labelling details.
Electrical Safety Procedures
Electrical safety procedures form the operational backbone of any safety program. Workers must know where disconnects, breakers, and panels are located so that energy can be removed quickly and deliberately when conditions demand it. In many facilities, clearly posting disconnect locations on serviced equipment reduces hesitation during emergencies and shortens response time.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Effective procedures do more than identify switches. They define verification steps, assign responsibility, and require confirmation that equipment is actually de-energized before work begins. Documented workplace safety procedures that are used, not just filed, create consistency across shifts and experience levels.
Lockout Tagout
Lockout Tagout refers to the structured control of hazardous energy during servicing and maintenance. When applied correctly, it prevents unexpected energization that can result in electrocution, arc flash, or mechanical injury. From an engineering standpoint, successful lockout systems depend on clear labelling, accessible isolation points, and equipment designs that support safe isolation. If you want a dedicated, step-by-step focus on what LOTO means in practice, start with Lockout Tagout.
The Electrical Safety Forum
The Electrical Safety Forum exists to support both qualified and non-qualified workers with current information on standards, regulations, products, and services. Electrical safety evolves as systems, technologies, and work practices change. Staying informed is not an academic exercise. It is how organizations avoid repeating the same preventable incidents under new conditions.