Power Quality
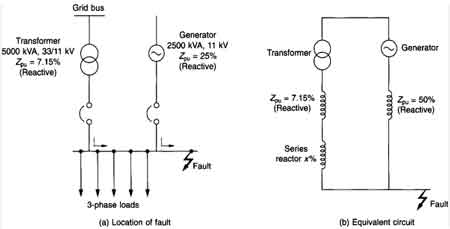
Reactor Reactance in Power System Explained
Download Our FREE Power Quality Handbook

Power Quality, Grounding & UPS Handbook Vol. 8
A valuable resource to installing and maintaining any electrical system.
The Power Quality, Grounding & UPS Handbook, Vol. 8 is a comprehensive guide that addresses these critical components of electrical infrastructure. This volume provides in-depth insights into the latest techniques and technologies for ensuring high-quality power, effective grounding systems, and reliable backup power solutions through UPS systems. Whether you're working in industrial, commercial, or data center environments, this handbook offers practical advice and solutions to help maintain a stable and secure electrical supply.
In this edition, we explore the various factors that affect power quality, including voltage fluctuations, harmonics, transient disturbances, and frequency deviations. We also provide detailed coverage on the design and implementation of effective grounding systems to protect both personnel and equipment. Additionally, Volume 8 offers expert guidance on selecting and maintaining UPS systems to ensure seamless power continuity during outages or disruptions.
This handbook includes case studies, troubleshooting tips, and step-by-step instructions for addressing power quality issues and grounding challenges. It also highlights the latest standards and regulations for grounding and UPS systems, ensuring that you stay compliant with industry guidelines.
Latest Power Quality Articles

Grounding A Generator
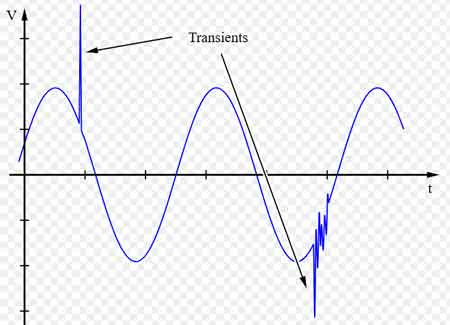
What is Transient Voltage?

Power Flickering: Causes and Prevention
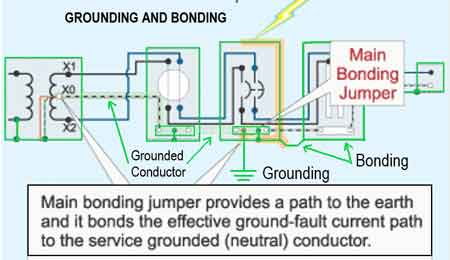
Grounding System - Electrical Fault Protection
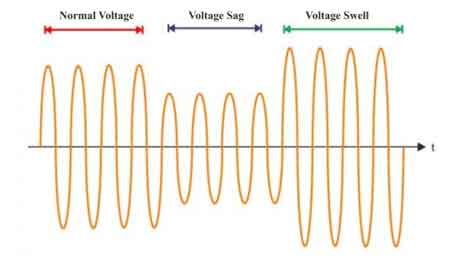
Voltage Sag