Construction Electrical Safety Practices

NFPA 70E Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards
- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
Construction electrical safety ensures OSHA compliance by using NFPA 70E and NEC guidelines, lockout/tagout, PPE, GFCI protection, grounding, arc-flash mitigation, insulated tools, and safe temporary power practices to control hazards on construction sites.
Principles of Construction Electrical Safety
Electrical construction safety is essential for protecting workers from serious hazards, including arc-flash incidents, electric shock, and contact with energized equipment. Construction sites' constantly changing, often unpredictable nature demands strict adherence to safety practices. On construction sites, compliance decisions are primarily shaped by OSHA electrical safety obligations rather than voluntary or advisory standards.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Adopting well-defined procedures, such as proper grounding, lockout/tagout protocols, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and compliance with standards like NFPA 70E and CSA Z462, plays a critical role in preventing injury, ensuring worker safety, and meeting regulatory obligations in both Canada and the United States. For a concise overview of minimum controls and compliance needs, see electrical safety requirements that translate standards into actionable steps.
Common Electrical Hazards on Job Sites
Construction sites present a variety of electrical risks. Workers may encounter energized circuits or unintentionally come into contact with overhead power lines. Equipment such as ladders or scaffolding can become deadly when it comes into contact with live conductors, especially if workers are unaware of the hazard. Additional dangers include the improper use of extension cords, damaged plugs, and poorly maintained temporary power sources. Even falls from height can result in electrocution if contact is made with exposed wiring or energized panels during the fall. Addressing these exposures within a formal program aligns with electrical safety in the workplace principles that emphasize hazard identification and controls.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Preventing Electrical Incidents on Construction Sites
Electrical and non-electrical workers must follow established safety procedures to minimize risks. Proper PPE—such as insulated gloves, face shields, and flame-resistant clothing—should be worn whenever there is a risk of electrical exposure. To ensure circuits are properly isolated, lockout/tagout procedures must be strictly followed when working on energized systems. Safety should be a team effort, with supervisors and foremen ensuring compliance and identifying potential hazards before work begins. Clear roles and documented procedures for qualified and unqualified persons are outlined in the electrical safety work guidance to support consistent execution.
All workers, especially those new to the electrical field, should receive comprehensive safety training to help them understand how to avoid dangerous situations. Employers must also implement safety programs that include regular inspections, the use of ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), and proper maintenance of grounding systems. Organizations can strengthen competencies through electrical safety training that combines theory with practical application.
Electrical Safety Standards and Training Requirements
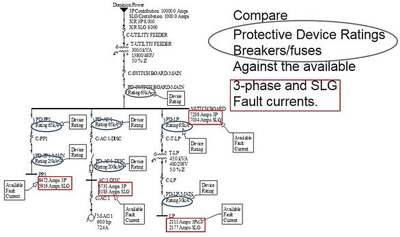
In the U.S., electrical safety on construction sites is governed by Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations. In Canada, similar standards are maintained by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), with CSA Z462 outlining specific requirements for arc-flash and electrical-hazard protection. Understanding how to determine incident energy and select PPE categories is central to the arc-flash training requirements many organizations incorporate into their policies.
Both NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 provide frameworks for evaluating risks, selecting appropriate PPE, and applying proper work methods around energized equipment. These standards are essential for any construction site safety program and should be integrated into company policies and daily practices. These methods are equally applicable in plant settings and in the process industries, in line with industrial electrical safety best practices.
Training Opportunities and Resources
The Electricity Forum offers specialized construction electrical safety training programs to ensure workers are equipped with the necessary knowledge. These include NFPA 70E training and CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training courses, designed to build awareness, strengthen safety practices, and support regulatory compliance across job sites in both Canada and the United States. Blended learning options and refresher modules are included in arc flash safety training resources to help maintain proficiency.
If you want to enhance your team’s safety readiness, request a free training quotation and find out how we can help you develop a safer, more compliant workforce.