Electrical Transformers

Isolation Transformer
Download Our FREE Electrical Transformers Handbook

Electrical Transformer Testing Handbook, Vol. 6
The better the efficiency of a transformer, the better your investment.
The Electrical Transformer Testing Handbook, Volume 6 provides a comprehensive guide to the testing, diagnosis, and maintenance of electrical transformers. This volume is designed for engineers, technicians, and maintenance professionals who are responsible for ensuring the reliability and safe operation of transformers in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. Whether you are working in a utility setting, industrial plant, or with renewable energy systems, this handbook offers essential insights and practical advice for all stages of transformer testing and maintenance.
In this edition, we explore the various methods and techniques used to test transformer performance, including insulation resistance testing, turns ratio testing, winding resistance measurements, and dielectric tests. We also cover key diagnostic procedures such as transformer oil analysis and partial discharge testing, which help identify early signs of damage or deterioration, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing the risk of failure.
Volume 6 delves into transformer fault detection, performance evaluation, and troubleshooting, providing a detailed understanding of common transformer issues such as winding faults, core saturation, and insulation breakdown. The handbook also addresses the latest advancements in transformer testing technologies, including online monitoring systems and automated diagnostic tools that enhance testing accuracy and efficiency.
Latest Electrical Transformers Articles
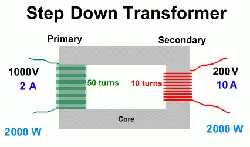
Step Down Transformers Reduce High Voltage
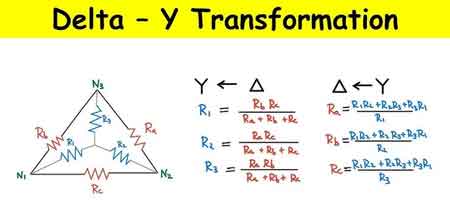
Delta to Wye Conversion

Potential Transformer Explained

How Much Electricity Does A High-Voltage Transformer Produce

Earthing Transformer - Safety and Stability
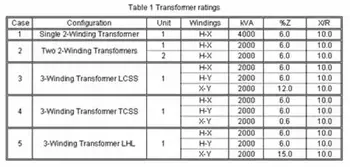
Transformer Ratings Explained
Electrical Transformers News
Electrical Transformers Media
Electrical Transformers Articles From ET Magazine

The Role of Transformer Oil Alternatives in Improving Safety and Environmental Sustainability

Enhancing Transformer Resilience: Fire Barriers and Safety Measures in Modern Substations

Navigating the Transformer Supply Crunch: Strategies for Utilities Amidst Global Shortages

MITIGATING TRANSFORMER FAILURES: ADVANCED MONITORING AND MAINTENANCE STRATEGIES
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue