Latest Utility Transformers Articles

Underground Transformer Explained
An underground transformer provides safe, efficient, and reliable voltage distribution in urban areas. Designed for compact installation, they reduce visual impact, enhance safety, and support power quality while integrating seamlessly with modern utility networks.
Underground Transformer Overview and Best Practices
In the intricate network of our electrical grid, transformers play a crucial role in converting high voltages from transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for distribution to homes and businesses. While the sight of towering overhead transformers atop utility poles is familiar to most, the underground transformer — including pad-mounted transformers, vault transformers, and submersible transformers — is a…
View more
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Utility Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Utility Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.

Dielectric Fluid
Dielectric fluid is an insulating liquid used in transformers, capacitors, and high-voltage equipment to prevent electrical breakdown while carrying heat away from energized components. Its dielectric strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance allow electrical systems to operate under high stress without arcing, overheating, or insulation failure.
In practice, dielectric fluid determines far more than whether insulation survives a laboratory test. It influences transformer loading limits, cooling behavior, aging rates, and the development of faults when insulation is stressed. In transformer applications, dielectric fluid works in tandem with transformer insulation to control electrical stress and long-term aging.
This article explores how dielectric fluids function…
View more

Reactors In Power System And Its Afffect On Transformer
Reactors in Power System and Its Afffect on Transformer mitigate fault current, damp inrush and transients, add series impedance, reduce harmonics, and enhance voltage regulation for grid stability and transformer protection.
Understanding Reactors in Power Systems and Their Effect on Transformers: Principles and Applications
Reactors in power systems control voltage levels, limit fault currents and improve power quality in utility transformers. These inductive components are strategically installed to manage reactive power, mitigate short-circuit currents, and reduce voltage fluctuations, ensuring the stability and efficiency of the electrical grid. Without reactors, transformers can experience excessive voltage stress, increased losses, and potential…
View more

Transformer Oil Filling
Transformer oil filling ensures proper insulation and cooling in power transformers. It involves degassing, dehydration, and vacuum filling of dielectric fluid to maintain system reliability, prevent overheating, and support high-voltage performance.
The Role of Transformer Oil Filling in Equipment Protection
Transformer oil filling is a critical process in the operation and maintenance of transformers within transmission and distribution (T&D) electrical networks. This specialized insulating oil serves as both a coolant and a dielectric medium, essential for dissipating heat and preventing electrical breakdowns. Proper oil filling ensures optimal transformer performance, enhances insulation properties, and extends the equipment's lifespan. In T&D…
View more

Typical Transformer Sizes
Typical transformer sizes span common kVA ratings, voltage classes, and single/three-phase units for distribution, industrial, and substation use, covering step-down power transformers from small residential loads to large utility applications.
Typical Transformer Sizes: Real-World Examples and Uses
Typical Transformer Sizes: A Guide to Selecting the Right Powerhouse for Your Needs
Transformers are the unsung heroes of electrical power systems, quietly working to step up or step down voltages, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. However, the wide range of available sizes and configurations can be daunting for those unfamiliar with the technical…
View more

How Many Volts Go Into a Distributor Bucket Transformer
How many volts go into a distributor bucket transformer? Typically, a pole-mounted distribution transformer takes 7.2-13.8 kV primary and steps down to 120/240 V service; values vary by utility feeder, region, and system design.
How Many Volts Go Into a Distributor Bucket Transformer?
How many volts go into a distributor bucket transformer? is a critical question for electrical engineering and maintenance professionals. Understanding the primary voltage levels applied to these transformers is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the safe and efficient operation of the electrical grid, minimizing the risk of equipment failure and power outages. Secondly, it…
View more
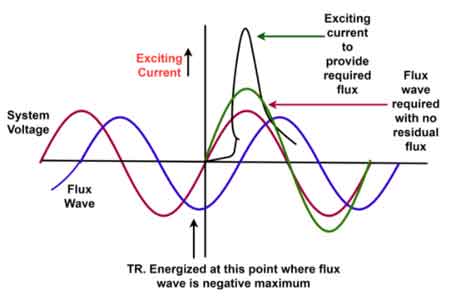
Excitation Current
Excitation current establishes transformer core flux and reflects magnetic losses, efficiency, and structural condition. Tracking its behavior helps detect core degradation, rising losses, and reliability risk long before visible failure occurs.
Excitation current is not a background electrical detail. In transformer operation, it is a diagnostic signal that reflects core magnetizing behavior, internal loss mechanisms, and early indications of structural or material change. Engineers and maintenance professionals rely on its behavior not to understand what a transformer is doing in theory, but to judge what is happening inside it in practice.
A transformer draws current even when its secondary is…
View more