Capacitance Definition
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Capacitance definition clarifies how a capacitor stores electric charge per unit voltage, measured in farads, influenced by plate area and dielectric, shaping reactance, energy storage, and signal behavior in AC and DC circuits.
Understanding Capacitance Definition: Principles and Applications
Capacitance Definition
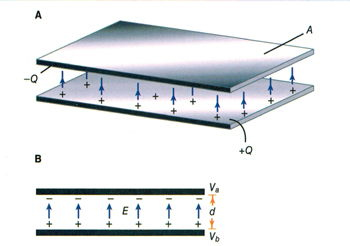
Another important property in AC electronic circuits, besides resistance and inductance, is capacitance. Capacitance is measured in units. The unit of capacitance is the farad. While inductance is represented in a circuit by a coil, capacitance is represented by a capacitor. In its most basic form, the capacitor is constructed of two parallel plates separated by a nonconductor, called a dielectric. In an electrical circuit, a capacitor serves as a reservoir or storehouse for electricity. For a clear overview of device construction and function, see what is a capacitor to relate these fundamentals.
Capacitance Definition in Direct Current
When a capacitor is connected across a source of direct current, such as a storage battery in the circuit shown in Figure 1A, and the switch is then closed, the plate marked B becomes positively charged, and the A plate negatively charged. Current flows in the external circuit when the electrons move from B to A. The current flow in the circuit is at a maximum when the switch is closed, but it continually decreases until it reaches zero. The current becomes zero as soon as the difference in voltage of A and B becomes the same as the applied voltages of the battery. The plates remain charged if the switch is opened, as shown in Figure 1B. Once the capacitor is shorted, it will discharge quickly as shown in Figure 1C. It should be clear that when the capacitor is being charged or discharged, there is current in the circuit, even though the gap between the capacitor plates breaks the circuit. Current is present only during the time of charge and discharge, which is usually short. A broader introduction is provided in what is capacitance for context on this charging behavior.
Fig 1 - Capacitance Definition in direct current.
The RC Time Constant The time required for a capacitor to attain a full electrical charge is proportional to the capacitance and the resistance of the circuit. The resistance of the circuit introduces the element of time into the charging and discharging of a capacitor. When designing filters or timing networks, combining devices affects total C, and capacitance in parallel explains how values add.
When a capacitior charges or discharges through a resistance, a certain amount of time is required for a full charge or discharge. The voltage across the capacitor will not change instantaneously. The rate of charging or discharging is determined by the circuit's time constant. The time constant of a series RC (resistor/ capacitor) circuit is a time interval that equals the product of the resistance in ohms and the capacitance in farad and is symbolized by the greek letter tau (τ). For a concise refresher on definitions and symbols, see capacitance before applying the time constant formula.
τ = RC
The time in the formula is required to charge to 63% of the voltage of the source. The time needed to bring the amount of charge to about 99% of the source voltage is approximately 5 τ. Figure 2 illustrates this relationship of the time constant characteristics of charging. In network calculations, series combinations behave differently, and capacitance in series outlines the reciprocal method used.
Fig 2 - Capacitance Definition discharge curve.
When asked for a capacitance definition, I often explain that capacitance is the measure of a capacitor’s ability to store electric charge. The symbol used for capacitance is the letter C. You can measure the electric potential of the dielectric material in an electronic component where it may store energy. For details on nomenclature and SI units, consult the unit of capacitance and confirm typical values.
As can be seen from the time constant illustration, there can be no continuous movement of direct current through a capacitor. A good capacitor will block
direct current and will pass the effects of pulsing DC or alternating current. For application examples across power supplies, signal coupling, and filtering, explore capacitors to see practical implementations.