Electricity How it Works
Electricity How It Works explains electron flow, voltage, current, resistance, and power in circuits, from generation to distribution, covering AC/DC systems, Ohm's law, conductors, semiconductors, transformers, and energy conversion efficiency and safety.
The Science Behind How Electricity Works
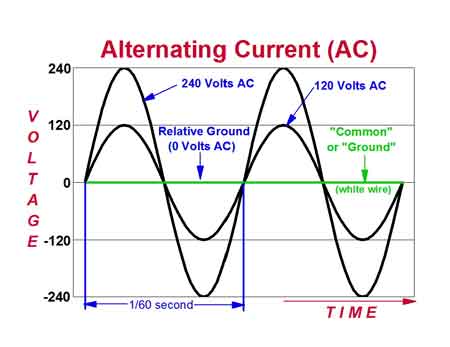
Electricity How It Works - This is a very common question. It can best be explained by stating this way: Single-phase electricity is what you have in your house. You generally talk about household electrical service as single-phase, 120-volt AC service. If you use an oscilloscope and look at the power found at a normal wall-plate outlet in your house, what you will find is that the power at the wall plate looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscillating power like this is generally referred to as AC, or alternating current. The alternative to AC is DC, or direct current. Batteries produce DC: A steady stream of electrons flows in one direction only, from the negative to the positive terminal of the battery.
For a refresher on fundamentals, the overview at what is electricity explains charge, current, and voltage in practical terms.
AC has at least three advantages over DC in an electricity power distribution grid:
1. Large electricity generators happen to generate AC naturally, so conversion to DC would involve an extra step.
2. Electrical Transformers must have alternating current to operate, and we will see that the power distribution grid depends on transformers.
3. It is easy to convert AC to DC but expensive to convert DC to AC, so if you were going to pick one or the other AC would be the better choice.
To connect these advantages to real-world practice, the primer on basic electricity clarifies AC versus DC behavior, impedance, and safety basics.
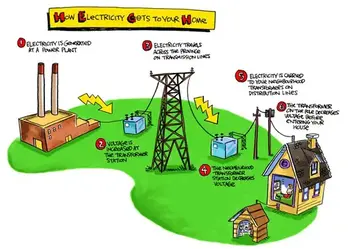
The electricity generating plant, therefore, produces AC. For a deeper look at how rotating machines induce AC, see the overview of electricity generators and their role in utility-scale plants.
Electricity How it Works in The Power Plant: Three-phase Power
If you want a quick walkthrough from generation to loads, this guide on how electricity works ties the concepts together before we examine three-phase specifics.
The power plant produces three different phases of AC power simultaneously, and the three phases are offset 120 degrees from each other. There are four wires coming out of every power plant: the three phases plus a neutral or ground common to all three. If you were to look at the three phases on a graph, they would look like this relative to ground:
A concise visual explainer on three-phase electricity shows how 120-degree phase offsets create balanced currents in feeders.
Electricity How It Works - There is nothing magical about three-phase power. It is simply three single phases synchronized and offset by 120 degrees. For wiring diagrams and common configurations, explore 3-phase power examples used across industrial facilities.
Why three phases? Why not one or two or four? In 1-phase and 2-phase electricity, there are 120 moments per second when a sine wave is crossing zero volts. In 3-phase power, at any given moment one of the three phases is nearing a peak. High-power 3-phase motors (used in industrial applications) and things like 3-phase welding equipment therefore have even power output. Four phases would not significantly improve things but would add a fourth wire, so 3-phase is the natural settling point.
Practical comparisons of motor torque ripple and line loading in 3-phase electricity help illustrate why three conductors strike the best balance.
And what about this "ground," as mentioned above? The power company essentially uses the earth as one of the wires in the electricity system. The earth is a pretty good conductor and it is huge, so it makes a good return path for electrons. (Car manufacturers do something similar; they use the metal body of the car as one of the wires in the car's electrical system and attach the negative pole of the battery to the car's body.) "Ground" in the power distribution grid is literally "the ground" that's all around you when you are walking outside. It is the dirt, rocks, groundwater, etc., of the earth.