Latest Electrical Transformers Articles
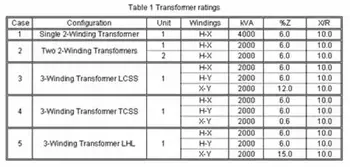
Transformer Ratings Explained
Transformer ratings define the electrical limits of transformers, including kVA capacity, voltage rating, current, frequency, and cooling class. These parameters ensure safe operation, efficiency, and reliability in power distribution and industrial systems.
Transformer ratings describe the operating limits that allow a transformer to perform safely and predictably in real electrical environments. These ratings summarize the voltage and current a unit can supply, its energy efficiency, and its heat management under load. Because every installation has different demands, choosing the right ratings is one of the most important decisions in system design.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a…
View more
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Different Types of Transformers
Different types of transformers include power, distribution, isolation, and instrument transformers. Each type serves unique roles in voltage regulation, electrical isolation, and energy transmission within power systems for industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Understanding Different Types of Transformers: Principles and Applications
Understanding the different types of transformers is vital for professionals responsible for designing, operating, and maintaining electrical infrastructure. Each type of transformer is engineered to perform specific functions, such as stepping up or stepping down voltage, isolating circuits, or providing accurate measurement and protection in substations. Mastering the differences between them enables electrical engineers and maintenance teams to…
View more

Control Transformer Explained
A control transformer provides a stable voltage to control circuits in industrial and commercial applications. It ensures reliable performance of contactors, relays, and motor starters by stepping down line voltage for safe, consistent control system operation.
Understanding How a Control Transformer Works
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
It is designed to provide a stable voltage for control circuits in various applications. This equipment reduces the supply voltage to a lower, more manageable level, suitable for controlling machinery and other electrical devices. Typically, the primary voltage is high, while the secondary voltage is…
View more

Transformer Testing Saves Money
Transformer testing evaluates insulation resistance, winding integrity, and load capacity to ensure efficiency, reliability, and safety. Routine diagnostic tests identify faults early, prevent downtime, and extend service life in electrical systems and power distribution networks.
Why Transformer Testing Matters in Power Distribution
Why Transformer Testing Matters
Electrical transformers play a crucial role in power distribution and transmission, converting voltage levels to meet the requirements of various electrical systems. Regular inspection is essential to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of these critical components. The primary purpose is to detect insulation breakdowns, winding faults, or voltage ratio discrepancies before they…
View more

Dry Type Transformers
Dry type transformers provide safe, efficient, and reliable electrical power distribution without the use of liquid insulation. Commonly employed in industrial, commercial, and residential systems, they reduce fire risk, require minimal maintenance.
Understanding Dry-Type Transformers: Principles and Applications
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
These transformers either step up voltage to higher levels or step down voltage for end-use distribution. In practice, they commonly reduce transmission voltages (for example, 500 kV) to distribution levels (30 kV for industrial systems or 120–240 V for residential loads). Because no flammable liquids are involved, they…
View more

Dry Type Transformer Types Explained
Dry type transformer types such as cast resin, VPI, and VPE provide safe, efficient, and eco-friendly voltage regulation for industrial, commercial, and renewable energy systems while reducing maintenance, fire, and environmental risks.
The Complete Guide to Dry-Type Transformer Types
Learn more about dry type transformers and their design principles, including how VPI and cast resin systems deliver safe, low-maintenance voltage regulation for industrial applications.
Dry type transformer types are essential components in modern power systems, providing efficient and fire-safe voltage regulation without relying on liquid insulation. Utilizing air or gas as the cooling medium, these transformers provide a sustainable…
View more

Capacitor Voltage Transformer Explained
A Capacitor Voltage Transformer (CVT) steps down high-voltage transmission levels for protection, metering, and control. Using a capacitive divider and electromagnetic unit, CVTs provide accurate, safe monitoring in power systems and substations.
How a Capacitor Voltage Transformer Works
A Capacitor Voltage Transformer (CVT) is a type of voltage transformer used in high-voltage (HV) substations to step down transmission line voltages for metering and protection purposes. It utilizes a capacitive voltage divider in conjunction with an electromagnetic voltage converter to provide a scaled-down replica of the HV signal, making it suitable for use in relay and measurement equipment. A CVT…
View more





