What is Medium Voltage iExplained
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

Medium voltage refers to electrical systems operating between 1 kV and 35 kV, used in industrial facilities, substations, and utility power distribution networks to safely transfer energy between low-voltage and high-voltage levels.
What is Medium Voltage?
A medium voltage (MV) system is crucial for distributing electricity in industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. It acts as the intermediary between high-voltage transmission lines and low-voltage consumer systems, ensuring efficient power delivery within a facility. This article provides a comprehensive overview of a medium voltage system, including its definition, applications, equipment, safety practices, and relevant standards. Understanding these concepts is vital for electrical professionals to ensure the safe and efficient operation of this critical power infrastructure. Medium voltage systems are essential links in 3 phase electricity networks, where balanced power delivery ensures efficient energy distribution across industrial and utility infrastructures.
Understanding medium voltage systems is essential for electrical professionals working in industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. This article provides a comprehensive overview of what constitutes medium voltage, its role in the power grid, common applications, and safety considerations. By grasping these key concepts, professionals can ensure the safe and efficient design, operation, and maintenance of these critical power systems. Understanding 3 phase power helps explain how medium voltage circuits maintain stable electrical loads in substations and manufacturing facilities.
Voltage Levels and Classifications
In the realm of electrical engineering, voltage levels are broadly categorized to distinguish their applications and safety requirements. These categories range from LV, typically used for residential applications, to extra high voltage (HV) and ultra-high voltages employed in HV transmission across long distances. MV occupies a middle ground, generally falling between 1,000 volts (600 volts in some instances) and 35,000 volts (35 kV). This distinguishes it from HV used in transmission and lower voltages used in end-user applications. Many 3 phase transformers and pad-mounted transformer installations operate at medium voltage levels, stepping electrical energy down for safe use in local distribution systems.
To better visualize this, imagine electricity flowing like a river through the electrical grid. V is like the force propelling the water, and different levels represent different sections of the river. HV is like a powerful, fast-flowing river capable of transporting electricity over long distances. MV, on the other hand, is like a branching stream that distributes the water (electricity) to various destinations. It's the crucial link between the high-powered transmission lines and the LV systems that deliver power to individual consumers. For a foundational understanding, review basic electricity concepts that explain how V, current, and resistance interact within medium voltage electrical systems.
What is Medium Voltage Applications?
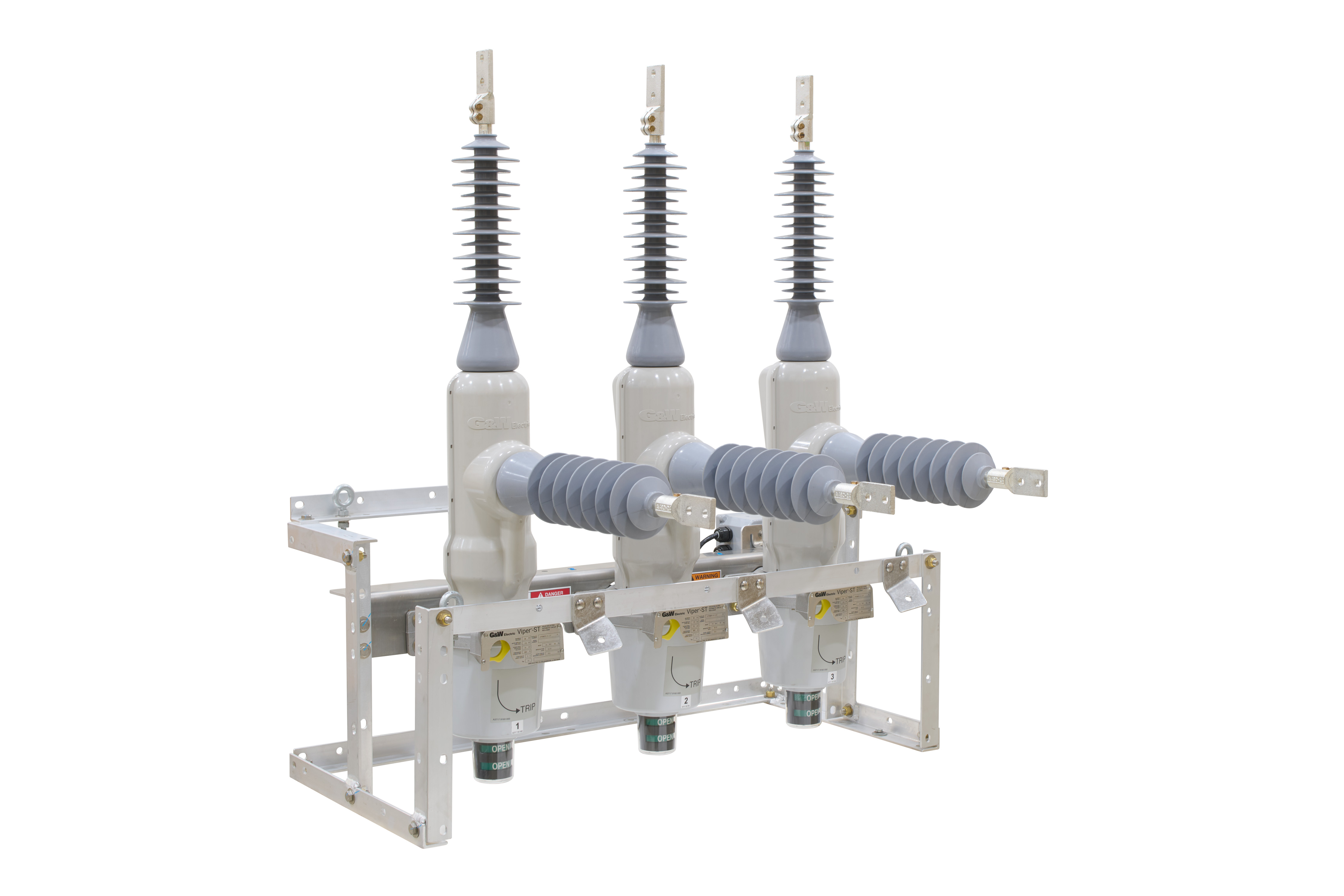
Medium voltage systems have a wide range of applications in industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. In industrial facilities, they power large motors, heavy machinery, and industrial processes. Commercial buildings utilize what is MV for HVAC systems, lighting, and other electrical loads. Institutions such as hospitals and universities rely on MV to support their critical operations.
The use of MV is increasing. Historically, it was mainly used for subtransmission and primary distribution, supplying distribution transformers that step down the voltage to LV for end-use equipment. It was also traditionally used in industries for MV motors. However, with advancements in power electronics and semiconductor technology, new applications are emerging, such as:
-
MV DC Distribution Grids: These grids offer higher efficiency in long-distance transmission and are being implemented in collector grids for wind and photovoltaic parks.
-
Renewable Energy Integration: MV systems play a vital role in integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid, enabling the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
The principles of active power apply directly to medium voltage operations, where real power flow efficiency determines the overall performance of industrial and commercial grids.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does MV differ from low and HV?
Medium voltage occupies a middle ground between LV, typically used for residential applications, and HV, employed for long-distance transmission. It's the "in-between" voltage level that allows us to efficiently distribute power to different consumers.
What is Medium Voltage Range ?
Generally, MV falls between 1,000 volts (600 volts in some instances) and 35,000 volts (35 kV). This range can vary slightly depending on regional standards and practices. For example, ANSI standards in the US include voltages up to 69 kV in the MV class, while IEC standards use 1000 Vrms as the threshold between low and HV in AC installations.
What is MV in industrial, commercial, and institutional power systems?
Medium voltage is distributed within these facilities to power various equipment and loads. It's the primary level used within these settings before being stepped down to LV for end-use.
What are common applications of MV systems?
Common applications include powering large motors and machinery in industrial settings, as well as HVAC and lighting systems in commercial buildings, and critical operations in institutions such as hospitals. Emerging applications include microgrids and the integration of renewable energy.
What are the key standards and regulations governing MV systems?
Key standards include those from ANSI, IEEE, and NEC, which provide guidelines for the design, installation, and safety of MV systems. These standards ensure that MV systems are implemented in a safe and consistent manner.
A Medium Voltage system is crucial for distributing electricity in industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. It acts as the intermediary between HV transmission lines and LV consumer systems, ensuring efficient power delivery within a facility. This article provides a comprehensive overview of a medium voltage system, including its definition, applications, equipment, safety practices, and relevant standards. Understanding these concepts is vital for electrical professionals to ensure the safe and efficient operation of this critical power infrastructure.