Electricity Prices Explained

Electricity prices reflect tariffs, kWh rates, time-of-use schedules, peak demand charges, and grid congestion, driven by generation costs, transmission losses, and load profiles in power systems and industrial electrical engineering.
The Complete Guide to Electricity Prices
Electricity prices, or rates, are usually determined by electric utilities and the governmental organizations that oversee them. The fees an electric utility company charges its customers for service aer based on electricity prices set by government, except in the case where they cost electricity prices on a deregulated basis. In that case, electricity prices are determined by marketplace factors such as supply and demand. Electric utility companies charge their customers different rates, depending on the type of customer, the kind of contract, and on the customer's needs. Electricity Prices bill energy on the kwh basis of the individual customer's rate, the level of consumption, and other charges, such as taxes and fuel adjustments. This is how electricity billed. For a deeper breakdown of typical rate components, resources like electricity cost guides explain line items and surcharges clearly.
That collection of rates is called a tariff. The power tariff is designed to provide the privately owned electric utility with enough income to allow investors to earn a cash return and cover operation and maintenance costs. Most of the larger utilities operate as regulated franchises, meaning that the prices they charge are subject to public review, often by a State public utility commission. In competitive markets, customers may choose an electricity supplier while the utility still handles delivery services and billing oversight.
Publicly owned electric utilities are nonprofit, local government agencies established to provide service to their communities and nearby consumers at cost, returning excess funds to the consumer in the form of community contributions, more economic and efficient facilities, and lower power rates. To meet these community objectives, public power agencies plan their electricity supply over multiyear horizons to manage risk and affordability.
Publicly owned electric utilities (which number approximately 2,000) include municipals, public power districts, State authorities, irrigation districts, and other State organizations. Some of these organizations also own or contract for electricity generation assets to enhance self-sufficiency and rate stability.
There are approximately 900 cooperative electric utilities in the United States currently doing business in 47 States. These utilities are owned by their members and are established to provide power to those members. Because member education supports better usage decisions, many cooperatives provide primers on what electricity is and how it is measured on bills.
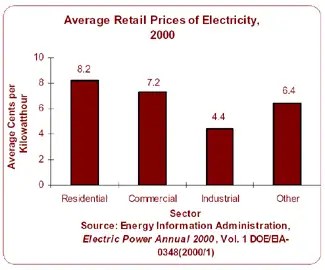
Average retail Electricity prices of power are calculated by dividing utility revenue by retail sales. The resulting measurement is the cost, or average revenue per kilowatthour, of power sold. (A kilowatthour is equal to one watt of power supplied to an electric circuit steadily for 1,000 hours.) Electric utilities usually offer three primary classes of service: residential, commercial, and industrial. The average price per kilowatthour for residential consumers is generally higher than for any other sector due in part to higher costs associated with serving many consumers who use relatively small amounts of power. In Ontario, the industrial sector has the lowest energy prices and energy bills rates every month due to the economies of serving a few consumers who use relatively large amounts of electricity. Understanding the distinction between energy in kilowatthours and instantaneous electricity power demand helps customers interpret peak charges and capacity fees. Regional consumption patterns, including trends in electricity demand in Canada, can influence wholesale prices and cross-border power flows affecting local rates.