What is a Photovoltaic Cell?
What is a photovoltaic cell? A semiconductor PN-junction device that converts sunlight to DC electricity via the photovoltaic effect, used in solar panels for renewable energy, power generation, efficiency optimization, and IV curve performance.
What Is a Photovoltaic Cell?
Photovoltaic cells are solid‑state electronic devices like transistors, diodes, and other components of modern electronic equipment. These devices are referred to as solid‑state because electrons flow through solid material within them. Most solar cells in use today are made from one of the most abundant materials on the planet, silicon, which is extracted from quartz and sand.
For a broader overview of how solar fits into the alternative energy landscape, the alternative energy solar power guide provides helpful context for newcomers.
Like all atoms, silicon atoms contain electrons that orbit around a central nucleus that contains protons and neutrons. In silicon, some of the electrons can be jolted loose from their orbit around the nuclei of the silicon atoms when struck by sunlight. These loose electrons can be made to flow together, creating an electrical current.These loose electrons can be made to flow together, creating an electrical current. Understanding how this microscopic process translates into real-world benefits and tradeoffs is central to the pros and cons of solar power that homeowners often weigh.
Because numerous solar cells are wired in series in a PV module, numerous electrons can be gathered up and conducted away from the array to power household loads. This module-level wiring is one part of a complete solar PV system that also includes racking, conductors, and balance-of-system hardware.
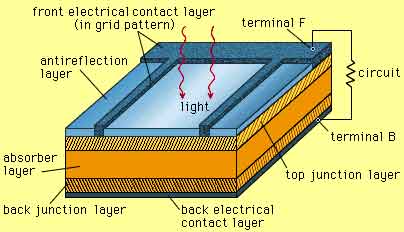
Most solar cells in use today are thin wafers of silicon about 1/100th of an inch thick (they range from 180 microns (μm) to 350 μm in thickness). As shown in Figure 1, most solar cells consist of two layers ‑ a very thin upper layer and a much thicker lower layer. The upper layer is made of silicon and phosphorus atoms; the bottom layer consists of silicon and boron atoms. These material choices underpin many advantages of solar power related to durability and scalability.
Fig1. Cross Section through a Solar Cell. Solar cells like the one shown here consist of two layers of photosensitive silicon, a thin top layer; the n‑layer; and a thicker bottom layer; the p‑layer. Sunlight causes electrons to flow from the cell through metallic contacts on the surface of most solar cells, creating DC electricity. Solar‑energized electrons then flow to loads where the solar energy they carry is used to power the loads. De‑energized electrons then flow back to the solar cell.
In remote applications, many designers consider off-grid solar power systems to ensure autonomy during grid outages.
When sunlight strikes the silicon atoms in solar cells, it jars electrons out of the atoms in both layers. These electrons flow preferentially toward the surface (for reasons beyond the scope of this book). These electrons flow into the metal contacts located on the front of solar cells. Numerous solar cells are wired in series in a solar module. Because of this, electrons extracted from one cell flow to the next cell, and then to the next cell, etc., until they reach the negative terminal of the module. Electrons flow from the array through wires connected to the house to power a load (any device that consumes electricity). After delivering the energy they gained from sunlight to the load, the de‑energized electrons return through a different wire to the array. The electrons then flow back into the solar cells, filling the empty spots left in the atoms created by their ejection. This permits the flow of electrons to continue ad infinitum. Before this DC electricity can serve typical household circuits, a solar power inverter converts it to AC safely and efficiently.
For extended resilience and load shifting, many systems integrate solar power batteries that store excess generation for use after sunset.





