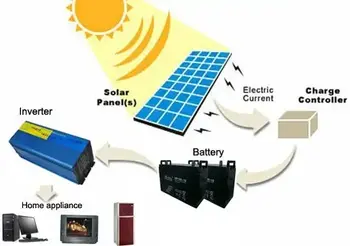
Solar Power Batteries

Solar power batteries store photovoltaic energy for off-grid and grid-tied systems, using lithium-ion cells, BMS, and inverters to deliver reliable backup power, peak shaving, and efficient AC/DC energy storage and microgrid applications.
Understanding How Solar Power Batteries Work
Flooded Lead Acid Batteries
Batteries used in most off‑grid renewable energy systems are deep‑cycle flooded lead‑acid batteries. These batteries can be charged and discharged (cycled) hundreds of times before they wear out. In many homestead and remote installations, these storage banks are paired with off-grid solar power systems to ensure consistent charging throughout varying weather.
Lead‑acid batteries contain three separate 2‑volt compartments, known as cells. Inside each cell is a series of thick parallel lead plates (Figure1). The cells are connected internally (wired in series) so that they produce 6‑volt electricity. The space between the plates is filled with sulfuric acid (hence the term "flooded"). A partition wall separates each cell, so that fluid cannot flow from one cell to the next. The cells are encased in a heavy‑duty plastic case. Within broader renewable energy systems used in remote sites, this rugged construction helps batteries withstand cycling and temperature swings.
As illustrated in Figure1, lead acid batteries contain two types of plates: positive and negative. The positive plates connect to a positive metal post or terminal; the negative plates connect to a negative post. The posts allow electricity to flow in and out of batteries. Because the output is direct current, integration with solar power inverters is required to supply standard AC loads safely.
Fig. 1: Anatomy of a Flooded Lead‑Acid Battery
The positive plates of lead‑acid batteries are made from lead dioxide (Pb02). The negative plates are made from pure lead. The sulfuric acid that fills the spaces between the plates is referred to as the electrolyte.
How Lead‑Acid Batteries Work
When used with photovoltaic arrays, charging current originates at the modules whose output is determined by the physics of photovoltaic cells and their exposure conditions.
Like all other types of batteries, lead‑acid batteries convert electrical energy into chemical energy when they are charged. When discharging, that is, giving off electricity, chemical energy is converted back into electricity. The chemical reactions that take place during battery discharge are shown in Figure 2. To prevent overcharge or excessive discharge during these cycles, systems employ solar power controllers that regulate voltage and current precisely.
As illustrated, when electricity is drawn from a lead‑acid battery, sulfuric acid reacts with the lead of the negative plates (top reaction). This reaction yields electrons, tiny negatively charged particles. They flow out of the battery creating an electrical current. During this reaction, lead on the surface of the negative plates is converted to tiny lead sulfate crystals. Proper array sizing within a complete solar PV system helps maintain discharge rates that minimize sulfation and extend service life.
Fig. 2: Chemical Reactions in a Lead‑Acid Battery.
When a battery is discharging, sulfuric acid also reacts with the lead dioxide of the positive plates, resulting in the formation of lead sulfate crystals on them as well (see bottom panel). Discharging a battery not only creates lead sulfate crystals on the positive and negative plates, it depletes the amount of sulfuric acid in the battery. When the battery is charged, however, lead sulfate crystals on the positive and negative plates are broken down, releasing sulfate ions into solution, thus replenishing the sulfuric acid. (The reactions that take place during recharge are the reverse of those that occur during discharge.)
Although the chemistry of lead‑acid batteries is a bit complicated, it is important to remember that this system works because electrons can be stored in the chemicals within the battery when a battery is charged. The stored electrons can be drawn out by reversing the chemical reactions. Through this reversible chemical reaction, the battery is acting as a"charge pump:' moving electrical charges through a circuit on demand. This stored energy can then be delivered through portable or stationary solar power generators to meet variable household or field demands.