Advantages of Solar Power

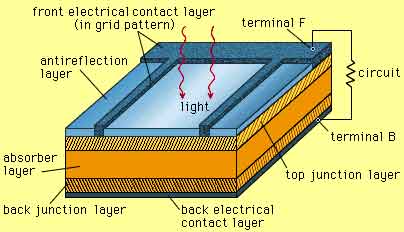
Advantages of solar power include high-efficiency photovoltaic systems, clean renewable energy, low O&M costs, grid integration with inverters and MPPT, distributed generation, net metering benefits, and improved resilience via energy storage and microgrids.
Key Concepts of the Advantages of Solar Power
Although solar electricity, like any fuel, has some downsides, they're clearly not insurmountable and, many believe, they are outweighed by their advantages. One of the most important advantages is that solar energy is an abundant, renewable resource. While natural gas, Oil, coal, and nuclear fuels are finite and on the decline, solar energy will be available to us as long as the Sun continues to shine ‑ for at least 5 billion years. For a broader context on trade-offs, see this solar power pros and cons overview that compares benefits and limitations in practical terms.
Solar energy is a clean energy resource, too. By reducing our reliance on coal‑fired power plants, solar electricity could help homeowners and businesses reduce their contribution to a host of environmental problems, among them acid rain, global climate change, habitat destruction, and species extinction. Solar electricity could even replace costly, environmentally risky nuclear power plants. Nuclear power plants cost upwards of $6 to $ billion, and no long term solution has been enacted to store the high‑level radioactive waste they produce. Additional background on how renewables mitigate pollution is outlined in this guide to renewable energy sources that highlights lifecycle impacts.
Solar energy could help us decrease our reliance on declining and costly supplies of fossil fuels like natural gas. Solar could also help us decrease our reliance on oil. Although very little electricity in the United States comes from oil, electricity generated by solar electric systems could be used to power electric or plug‑in hybrid cars and trucks, reducing our demand for gasoline and diesel fuel, both of which come from oil. And, although the production of solar electric systems does have its impacts, all in all it is a relatively benign technology compared to fossil fuel and nuclear power plants. As transportation electrifies, insights on alternative energy power can help consumers plan charging and efficiency.
Another benefit of solar electricity is that, unlike oil, coal, and nuclear energy, the fuel is free. Moreover, solar energy is not owned or controlled by hostile foreign states or one of the dozen or so influential energy companies that largely dictate energy policy, especially in the United States. Because the fuel is free and will remain so, solar energy can provide a hedge against inflation, caused in part by ever‑increasing fuel costs. For policymakers, curated alternative energy solutions illustrate market mechanisms that stabilize costs.
An increasing reliance on solar and wind energy could also ease political tensions worldwide. Solar and other renewable energy resources could alleviate the need for costly military operations aimed at stabilizing the Mideast, a region where the largest oil reserves reside. Because the Sun is not owned or controlled by the Middle East, we'll never fight a war over solar or other renewable energy resources. Not a drop of human blood will be shed to ensure a steady supply of solar energy to fuel our economy. Understanding diverse forms of alternative energy also clarifies how energy diversity reduces geopolitical risk.
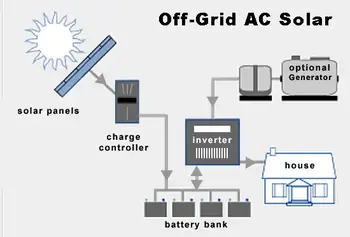
Yet another advantage of solar‑generated electricity is that it uses existing infrastructure ‑ the electrical grid ‑ and technologies in use today such as electric toasters, microwaves, and the like. A transition to solar electricity could occur fairly seamlessly. Grid integration best practices and alternative energy solar power case studies show how adoption can proceed with minimal disruption.
Solar electricity is also modular. You can add on to a system over time. If you can only afford a small system, you can start small and expand your system as money becomes available. Homeowners exploring upgrades can consult resources on renewable alternative energy to plan phased system expansions.
Solar electricity could provide substantial economic benefits for local, state, and regional economies. And solar electricity does not require extensive use of water, an increasing problem for coal, nuclear, and gas‑fired power plants, particularly in the western United States and in and regions.