Voltage Drop Calculator
By William Conklin, Associate Editor
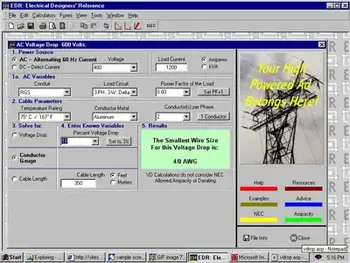
A voltage drop calculator estimates the voltage loss in an electrical circuit based on conductor length, load current, wire size, and material. It allows electricians and engineers to verify that circuits will deliver usable voltage to equipment while staying within accepted design and code limits.
In real installations, voltage drop is not just a theoretical number. Excessive drop causes motors to overheat, controls to malfunction, and lighting to underperform. The calculator exists to prevent those outcomes before conductors are installed, not after problems appear in the field.
By translating resistance, distance, and load into a measurable loss value, a voltage drop calculator turns conductor selection from a rule-of-thumb decision into a controlled engineering choice. It helps designers balance efficiency, reliability, and compliance in both power and control circuits.
How a Voltage Drop Calculator Works in Practice
A voltage drop calculator calculates the voltage drop as current flows from the source to the load. Users enter conductor length, load current, conductor material, and wire size. The calculator applies resistance relationships to determine whether the resulting voltage drop stays within acceptable operating limits.
This allows designers to confirm that circuits will perform as intended under real operating conditions. Instead of discovering voltage problems after installation, the calculator supports correct cable sizing, conductor selection, and system layout decisions at the design stage. For those who want to examine the underlying math, the voltage drop formula for AC and DC circuits explains how a conductor's resistance, current, and length combine to produce voltage drop.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
Applications of Voltage Drop Calculators
In residential work, they help determine proper wire sizing for branch circuits and feeders, especially when distances increase. Long runs to garages, outbuildings, or outdoor equipment often require careful evaluation to avoid nuisance problems and reduced appliance performance.
In commercial buildings such as offices, hospitals, and schools, voltage drop calculations support the reliable operation of lighting, HVAC systems, and sensitive electronic equipment. These environments demand consistent voltage delivery to protect both occupants and infrastructure.
In industrial settings, voltage drop calculators are essential for motor circuits, process equipment, and high-load installations. Accurate calculations help ensure that machinery starts correctly, operates efficiently, and does not place unnecessary stress on electrical components.
Benefits of Using a VDC
Using a voltage drop calculator provides clear advantages during electrical design and troubleshooting.
-
It improves accuracy by replacing guesswork with calculation based on real circuit conditions.
-
It saves time by automating complex evaluations that would otherwise require manual formulas.
-
It helps control costs by preventing oversized conductors while avoiding under-designed circuits.
-
It supports safety by reducing the risk of overheating, equipment malfunction, and electrical hazards.
Cable Sizing and Wire Gauge
Conductor size plays a major role in voltage drop. Smaller wires have higher resistance, which increases voltage loss as current increases or the distance increases. Selecting the correct wire gauge ensures that conductors can carry the intended load without excessive losses or thermal stress.
American Wire Gauge standards provide a consistent reference for conductor sizing, while electrical codes offer guidance on acceptable voltage drop levels for different applications. These references work together to support safe and efficient system design.
Copper or Aluminum Conductors
Conductor material also affects the voltage drop. Copper is commonly used for its lower resistance and higher conductivity, resulting in less voltage loss for a given size. Aluminum, while having higher resistance, is lighter and more cost-effective for larger conductors and longer runs.
A voltage drop calculator helps account for these material differences so designers can make informed tradeoffs between performance, cost, and installation requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I calculate voltage drop?
Voltage drop is calculated using the relationship between current, resistance, and conductor length. Ohm’s Law provides the foundation for this calculation.
Why is voltage drop important?
Excessive voltage drop can cause poor equipment performance, overheating, and safety concerns. Managing it helps protect both systems and people.
What is an acceptable voltage drop?
A common guideline is a maximum of 3% for branch circuits and 5% total for feeders and branch circuits combined, based on NEC recommendations.
Are voltage drop calculators always accurate?
Their accuracy depends on the correctness of the input values. Factors such as temperature, installation method, and operating conditions may require additional engineering judgment.
Related Articles

_1497175164.webp)