Total Impedance Calculator
Total impedance calculator determines total opposition in AC circuits by combining resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance. Input R, L, C, and frequency to find Z in ohms for accurate analysis in power distribution, filters, or signal systems.
Total Impedance Calculator: Real-World Examples and Uses
A total impedance calculator helps you quickly determine the combined impedance of resistors, inductors, and capacitors in AC circuits. By inputting values for resistance (R), inductive reactance (XL), and capacitive reactance (XC), you can calculate total impedance (Z) for both series and parallel configurations, making circuit analysis faster, more accurate, and easier to understand. A total impedance calculator is a powerful tool used by electrical engineers, technicians, and students to determine the impedance in RLC circuits, whether in series or parallel. These calculators simplify complex calculations involving resistance, inductance, and capacitance by processing formulas that would otherwise require manual computation with complex numbers.
Whether you are designing a power supply, analyzing signal transmission, or optimizing filter performance, a total impedance calculator helps ensure accuracy and efficiency. It is especially valuable when analyzing the behaviour of AC circuits across different frequency ranges in hertz.
What Is Total Impedance?
Total impedance refers to the combined opposition that a circuit presents to the flow of alternating current. It takes into account both resistance (R) and reactance (X), expressed as a single value in ohm (Ω). The two primary types of reactance are:
-
Inductive reactance (caused by coils or inductors)
-
Capacitive reactance (caused by capacitors)
These values change depending on the circuit's frequency, making tools like a total impedance calculator essential for real-time circuit analysis.
Who Uses a Total Impedance Calculator?
-
Electrical engineers use it in power systems, communications, and control circuits.
-
Technicians rely on it to verify component ratings and troubleshoot systems.
-
Educators and students apply it in academic settings for lab work and theoretical analysis.
-
Industrial maintenance professionals use it to evaluate equipment behavior under various loads.
It is particularly helpful when working with an RLC circuit impedance calculation where both inductance (L) and capacitance (C) are present.
What Does a Total Impedance Calculator Do?
A good impedance calculator lets you:
-
Enter known values like resistance (R), inductance L and capacitance C, and frequency in hertz.
-
Automatically compute impedance for either series RLC circuit or parallel RLC circuit setups.
-
Show results using the correct impedance formula, including both magnitude and phase.
-
Factor in angular frequency in rad, derived from ω=2πf\omega = 2\pi fω=2πf, where fff is frequency.
-
Solve expressions like 1ωC\frac{1}{\omega C}ωC1 or frac 1 omega, commonly used in capacitive reactance calculations.
The result is a fast, accurate way to determine the impedance and analyze AC circuit behavior.
Key Concepts Behind the Calculator
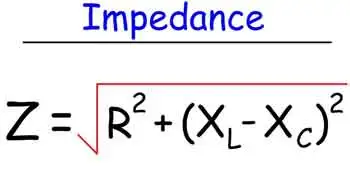
1. Impedance Formula (Z)
This requires working with complex numbers to calculate both magnitude and phase angle.
2. Reactance Components
-
Inductor and capacitor components contribute to the reactive part of the impedance.
-
Capacitive reactance
-
Inductive reactance
These values vary with frequency and affect circuit resonance and behavior.
Why Use a Total Impedance Calculator?
Without a calculator, these formulas can be tedious to evaluate manually—especially when working in real time or across wide frequency in hertz ranges. A calculator ensures:
-
Greater accuracy in design and testing
-
Time-saving analysis for troubleshooting
-
Safer decision-making for load balancing and component selection
In power electronics, knowing the rlc circuit impedance helps prevent equipment damage and improves system efficiency.
A total impedance calculator is an essential tool for modern electrical work. It brings together the core principles of AC circuit analysis—resistance, inductance, capacitance, and frequency—into one user-friendly interface. Whether you're designing systems, teaching students, or maintaining equipment, using this tool helps you quickly and reliably calculate the impedance and make informed decisions.
Related Articles