Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems integrate solar PV, wind turbines, battery storage, inverters, and smart grid controls for efficient generation, power conversion, and grid integration, enabling resilient microgrids and low-carbon, distributed electricity.
Renewable Energy Systems: Real-World Examples and Uses
Renewable energy systems today can be a cost effective alternative for areas with high electricity connection fees. For an overview of how stand-alone configurations work in remote areas, see this guide to off-grid solar power systems and typical cost considerations.
It is also possible to connect renewable energy power systems to the grid, reducing the amount of electricity you need to purchase, or in some cases, allowing you to export surplus power into the grid. Many homeowners start with a basic solar PV system to offset daytime loads before expanding capacity.
About renewable energy systems
Renewable energy is energy produced from sources which can be replenished or replaced from natural sources. For a deeper introduction, explore this overview of renewable energy and common technologies.
The most common forms of renewable energy used include:
- photovoltaic modules;
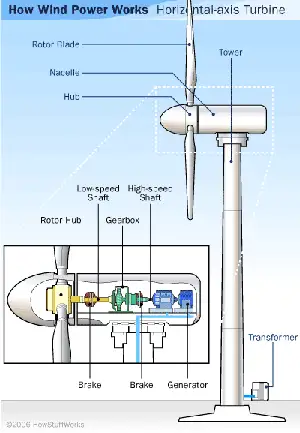
- wind turbine generators; and
- micro hydro generators.
Homes usually are serviced with electricity from any of these renewable energy systems on their own or in combination with other electric power systems. Resources on broader renewable alternative energy can help you compare options for your site.
Grid-interactive vs. stand-alone power supplies
Since renewable energy systems are often intermittent, (because solar panels only operate during daylight and mostly sunny days) a method of storing the electricity is required. The most common solution for this situation is to incorporate the use of storage batteries. Power from the solar array is used to charge batteries for use later in the day. Because these systems work independently from the electricity grid, they are often referred to as "stand alone power systems". In situations where the cost of connection to the power grid is prohibitive, a stand-alone renewable energy system can be cost effective. Many stand-alone systems use diesel or gasoline generators to recharge batteries during extended period without solar energy.
When planning capacity, it's helpful to weigh the pros and cons of solar power for your climate and usage profile.
An alternative is to use the electricity grid to store the energy. These systems are known as grid-interactive systems. The renewable energy is converted to electricity for use in the household and any surplus power is fed into the grid. Power is drawn from the grid when the renewable energy system is not enough to meet the home's energy demand. Some electric utilities prefer that all of the power from the solar power system is sent directly to the grid and metered separately , which means that all the electricity to the home comes from the grid as it is with conventional homes.
Components and features of stand-alone renewable energy systems.
Renewable energy systems consist of several very basic component equipment parts and there are key features which are briefly described and shown on this page.
- Electric Power Generating Equipment
- PV modules, wind turbines, micro-hydro generators, or a petrol or diesel generator can provide electric power production on their own or in concert with other systems.
- Control and regulation equipment
- Various types of power regulators, controllers, power meters and power circuit breakers may be used to control battery charging and to provide power protection.
- Energy storage
- Specialized large capacity batteries are usually used to store otherwise lost energy so that a reliable source of power can be available when needed.
- Inverters
- These devices convert electricity from the batteries or renewable energy source to the electricity used by household appliances (240 V AC).
- Specialized “grid-interactive” inverters are able to feed electricity produced by renewable sources into the electricity grid without disruption to the household electricity supply.
- Control Box
- Wiring and electrical accessories
Well-designed renewable energy systems should include special wiring that is capable of keeping energy losses to an absolute minimum. Adequate power fusing, electrical grounding, lightning protection and other measures should be used in the renewable energy system.
- Home design, lighting and various appliances
TNew home designs should incorporate useful energy efficiency features. Also, high efficienct lighting systems and appliances can be selected and specified to keep the energy load to a bare minimum, thus aiding to reduce the cost of such systems.
Grid-interactive renewable energy power systems
In addition to stand-alone systems, which require batteries to store energy, REPS can operate in conjunction with the mains electricity system. These are known as grid-interactive or grid-connected systems.
How do they work?
In grid-interactive renewable energy systems electricity is still generated from a renewable energy source in the same way as a stand-alone system. The electricity generated then passes through a specially approved power inverter, which converts electric energy into conventional 240 V which in turn is used by home appliances. When there is surplus electricity generated, it will be sent back through the inverter into the power grid. If the home consumes more electricity than your renewable energy system is producing, the power provider automatically will supply the balance of the energy required without any disruption to home appliances. Selecting a certified solar power inverter ensures grid compliance and optimal performance.
Your power meter measures the level of outgoing and incoming electricity. This provides a net usage amount for your house. In the majority of cases, surplus electricity which is fed back to the electric utility is credited back to you. The net amount that is actual consumption is charged for that billing period. In reality, your power meter can become a cash register. Specialized "smart" meters are sometimes used where more detailed power monitoring is required. As there are variations to this process, check with your electricity supplier for more information on equipment and metering details for your property.
What are the benefits?
The major benefit of grid-interactive renewable energy systems is that they produce power from clean, renewable solar energy, allowing householders to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve our environment. As renewable energy systems use the main electricity grid as a back-up, power is always available and systems can be sized according to the customer’s requirements and budget. For background on technologies and policy, review renewable energy facts for informed decision-making.