Latest Smart Grid Articles
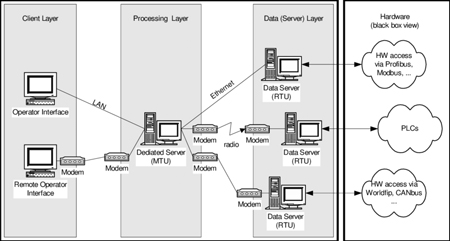
SCADA Architecture
SCADA architecture describes how field devices, control networks, and supervisory software are organized to monitor, automate, and manage industrial and utility systems, supporting real-time visibility, reliable communication, and coordinated control.
SCADA Architecture – System Design
Supervisory control and data acquisition systems do not succeed or fail on software alone. Their reliability is shaped by how sensors, controllers, communication paths, and operator tools are arranged into a coherent structure. SCADA architecture is the framework that enables this coordination, especially in environments where equipment is geographically dispersed, and operational decisions must be made quickly and with confidence.
In practice, architecture decisions…
View more
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Smart Grid Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Smart Grid Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
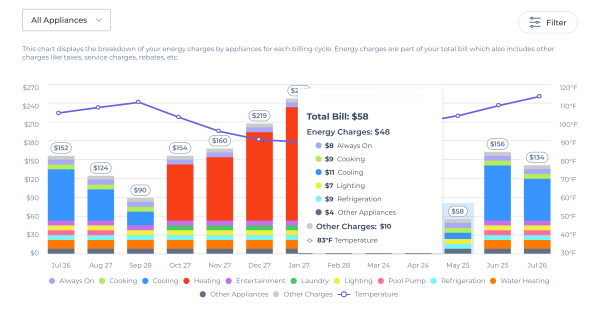
Vertical AI for Utilities: Solving the High-Bill Crisis in Ways Your Legacy AI Tools Can’t
Vertical AI helps utilities explain high energy bills by turning smart meter data into appliance level insights, cutting call handle time, improving first call resolution, and restoring customer trust.
The headlines are everywhere, and utility customers are feeling the pinch. A recent poll found that 62 percent of Americans are seeing their energy bills jump, and a staggering 73 percent fear those costs will keep climbing. This isn't just an inconvenience, it's a crisis of confidence for utilities.
When a customer gets a high bill, their first reaction is to call you. This surge in calls chokes utility customer service…
View more
Role of Data Analytics in Operational Efficiencies and as Sustainable Future
Data analytics in electrical engineering leverages machine learning, time-series modeling, and anomaly detection on SCADA and IoT big data to optimize power systems, signal processing, predictive maintenance, and real-time grid reliability.
Understanding Data Analytics: Principles and Applications
Mobile, social, cloud, analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are driving the digital transformation in utilities creating new opportunities to optimize operations, and integrate the utility customer into the energy and water value chain. With the global focus on sustainability, these technologies are becoming increasingly central to achieving the energy efficiency and water conservation goals.Dawn of a New ‘Data’ AgeAcross all…
View more

Improved Sensor Technology Explained
Improved sensor technology enhances accuracy, sensitivity, and reliability in electrical engineering, leveraging MEMS, IoT connectivity, advanced signal processing, calibration, and low-noise analog front-ends for superior data acquisition, diagnostics, and energy-efficient embedded systems.
How Improved Sensor Technology Works
BACKGROUND
Many countries rely on diesel generation, coal, or hydropower to generate electricity. However, these generation methods aren’t keeping up with demand due to urbanization, a growing middle class, electrification of heating sectors, electric vehicles, and heat pumps. While prices for energy haven’t risen at the same rate as in other countries, it does contribute to a rise in inflation. As these…
View more
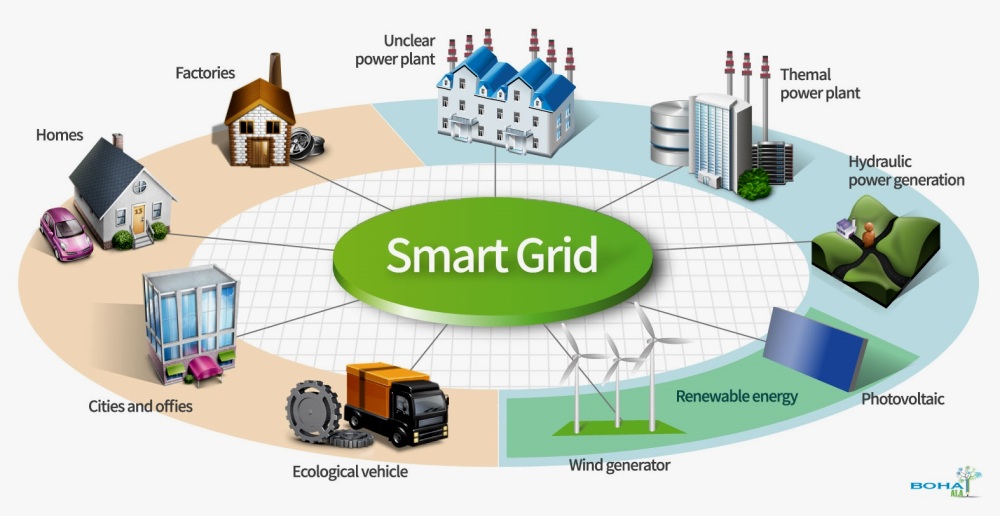
Grid Modernization Explained
Grid modernization improves the electric power system with smart technologies, automation, and renewable integration. It enhances grid reliability, resilience, and efficiency while enabling two-way communication, distributed energy resources, and better outage response for future-ready power delivery.
Understanding Grid Modernization?
Grid modernization is the process of upgrading the electric grid with intelligent systems to improve reliability, resilience, and efficiency. Grid modernization builds on the broader foundation of the Smart Grid, where digital communication, automation, and real-time control improve how utilities plan, operate, and protect the power system.
We can build a more sustainable, resilient, and efficient power grid by integrating…
View more
DHS/FBI Alert: Russian Government Cyber Activity Targeting Power Grid
DHS FBI Alert provides a joint advisory and threat bulletin on cybersecurity, terrorism risks, and critical infrastructure protection, offering mitigation guidance, IOCs, and timely warnings to enhance public safety and incident response.
Quick Reference: DHS-FBI Alert
In an unprecedented alert, the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and FBI have warned of persistent attacks by Russian government hackers on critical US government sectors, including energy, nuclear, commercial facilities, water, aviation and manufacturing.The alert details numerous attempts extending back to March 2016 when Russian cyber operatives targeted US government and infrastructure.The DHS and FBI said: “DHS and FBI characterise this…
View more
_1752206400.jpg)
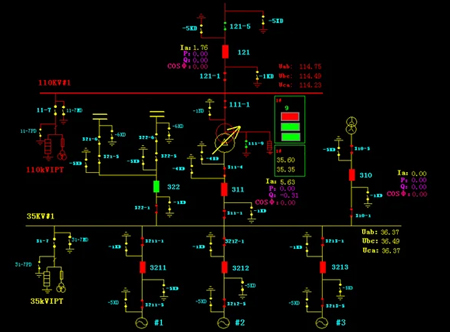
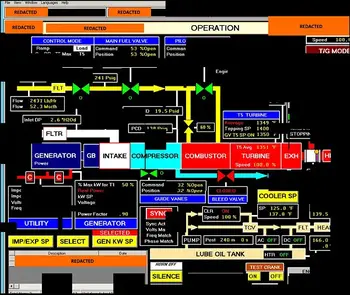
What is SCADA?
SCADA is a utility-grade system that enables real-time grid monitoring, remote control, fault detection, and substation automation. It improves electric utility reliability, safety, and performance through centralized supervision and smart data collection.
What is SCADA?
Key Functions of SCADA in Utilities
In today’s power systems, real-time control, automation, and visibility are not optional—they’re essential. SCADA systems make this possible. For electric utilities, SCADA serves as the digital nervous system, connecting control centers with field equipment spread across substations, switchyards, feeders, and beyond. It turns dispersed infrastructure into a responsive, manageable network.
Rather than being a single tool or…
View more