Latest Overhead T&D Articles

Fault Indicator Explained
A fault indicator is an electrical device that detects and displays fault conditions in power systems. Used in distribution networks and switchgear, it improves fault detection, outage response, and grid reliability while supporting predictive maintenance.
Fault Indicator: Real-World Examples and Uses
Understanding how this device functions and its role in maintaining a reliable power system is crucial for any electrician working in an industrial setting. Let’s explore the core concepts, their various applications, and the benefits they offer in terms of issue location, outage reduction, and overall system reliability. By reading this article, an industrial electrician will gain valuable…
View more
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Overhead T&D Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Overhead T&D Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.

Electrical Insulator Explained
Electrical insulator materials resist current flow to protect people and equipment. Used in power transmission and switchgear, electrical insulators rely on high resistivity, dielectric strength, and breakdown voltage to prevent leakage.
Electric power only works when it stays inside its intended path. An electrical insulator exists to make sure it does. Unlike conductors, which are chosen to carry current, it is chosen because it prevents current from passing.
In real systems, an electrical insulator separates energized components from grounded structures, confines electric fields within equipment, and prevents accidental discharge. When insulation fails, electricity does not quietly drift. It escapes violently,…
View more

High Voltage AC Transmission Lines
Ac transmission lines deliver alternating current across the power grid using high voltage, overhead conductors, and insulators, controlling reactive power, impedance, and corona effects to minimize losses, improve efficiency, and ensure reliable long-distance electricity transmission.
Understanding the Role of AC Transmission Lines in Power Systems
Three-phase electric power systems are used for high and extra-high voltage AC transmission lines (50kV and above). The pylons must therefore be designed to carry three (or multiples of three) conductors. The towers are usually steel lattices or trusses (wooden structures are used in Germany in exceptional cases) and the insulators are generally glass…
View more
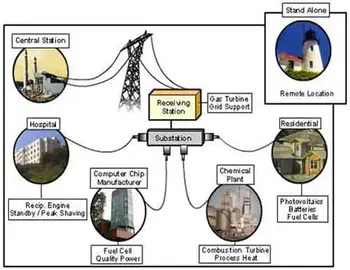
Distributed Energy Resources - Small Scale Power
Distributed energy resources integrate rooftop solar, battery storage, EV charging, and demand response within microgrids and virtual power plants to optimize load, enhance grid resilience, lower costs, and enable real-time, bidirectional power flows.
Why Distributed Energy Resources Matter in Power Distribution
Distributed energy resources (DERs) can benefit the power system and individual homes and businesses. DERs can increase the resiliency and reliability of the power grid, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, reduce the overall power cost, and provide power at the point of use. Several types of DERs can be used to generate electricity, including renewable energy sources like solar…
View more

Electric Power Distribution
Electric power distribution delivers electricity from substations to homes, businesses, and industries, using transformers, feeders, and circuits to maintain voltage stability, ensure reliability, and support safe, efficient energy delivery.
Electric Power Distribution: Real-World Examples and Uses
Distribution systems are a subset of the larger grid, linking transmission lines, substations, transformers, and service drops into a cohesive network. Their design must ensure voltage regulation, load balancing, and service continuity, even under fault conditions or peak load demand. Modern electrical distribution systems combine traditional infrastructure with advanced monitoring to ensure safe and efficient energy delivery.
Core Components of the Distribution System
Transformers…
View more
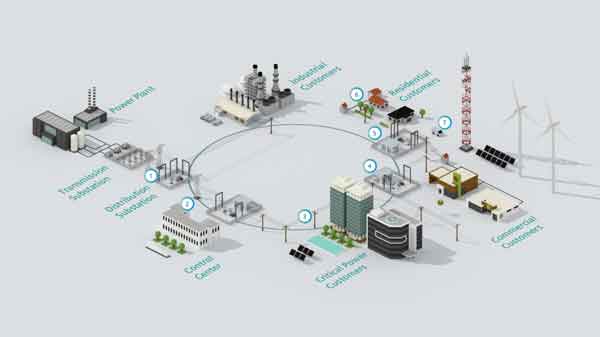
Distribution Automation Reliability
Distribution automation enhances grid reliability, efficiency, and fault detection using smart sensors, communication networks, and control systems. It supports smart grid operations, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent, safe power delivery.
Applications of Distribution Automation in Modern Power Systems
Distribution automation is a vital component of smart grid modernization, enabling utilities to create more reliable, efficient, and adaptable power networks.
The Role of Distribution Automation in Power Systems
Distribution automation is one of the most important technologies driving the modernization of transmission and distribution (T&D) grids. By integrating sensors, communication networks, control devices, and software platforms, utilities can optimize performance, manage the integration…
View more
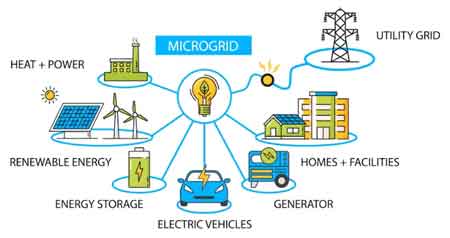
What is a Microgrid?
A microgrid is a localized energy system that can operate independently of or in conjunction with the main grid. By integrating renewable energy, storage, and smart controls, it enhances reliability, supports sustainability, and provides backup power for critical facilities.
What is a Microgrid?
Microgrids are gaining popularity as reliable and efficient solutions for modern energy challenges. They are increasingly valuable as the world pursues cleaner energy sources, carbon reduction, and grid modernization. By complementing smart grid infrastructure, they improve system reliability while helping communities and industries adapt to the demands of today’s evolving power networks.
What Defines…
View more